Research
Turbulent Heat Transfer Measurements Using Infrared Thermography
【 Outline 】
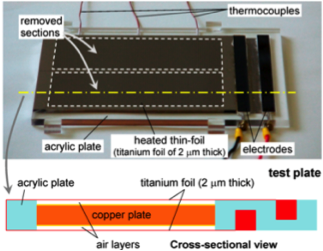
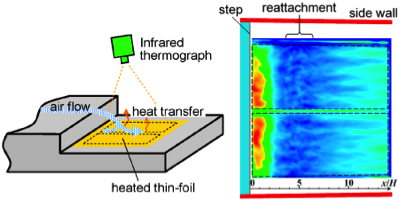
We have developed a measurement technique using high-speed infrared thermography to investigate the unsteady mechanism of convective heat transfer. This technique makes it possible to visually observe the spatiotemporal behavior of heat transfer as a movie, which could never be obsetved by point measurements such as thermocouples.
To date, we have performed the following: (1) Derivation of analytical solution concerning the frequency-response and spatial-resolution of measurements; (2) Design and experimental demonstration of a test model which can quantitatively measure the spatiotemporal variation of heat transfer; and (3) Measurements of heat transfer to the airflow for a turbulent boundary layer and for separated and reattached flows. The results demonstrate that convective heat transfer actually fluctuates in very complicated manners temporally and spatially, due to flow turbulence. Although the variation of heat transfer appears to be random, it was clarified to have some periodicity in the spatial distribution corresponding to, for example, the streak structure of wall turbulence.
Subsquently, we have tried to measure spatiotemporal velocity field near the wall using PIV simultaneously with the heat transfer measurement to clarify the relationship between turbulent vortex structures and heat transfer.
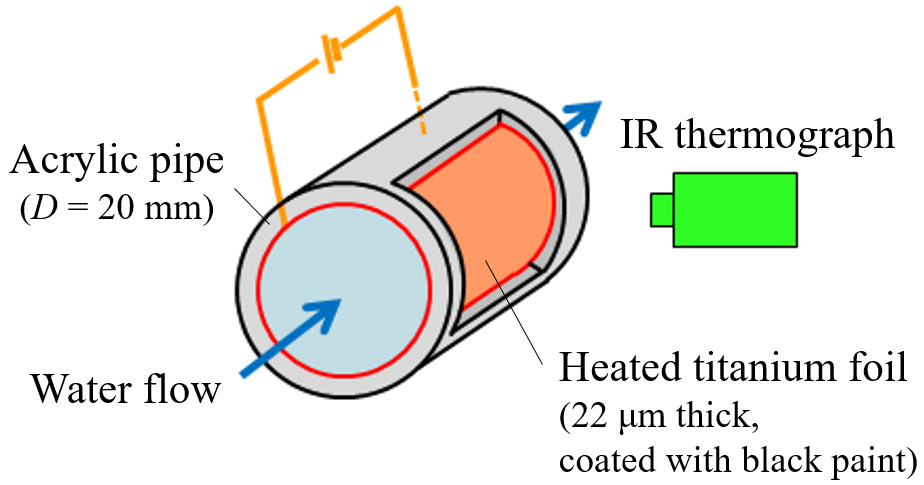
We have also performed to measure the flow in a circular pipe using water as the fluid. Through these measurements, we have been conducting researches for separated and reattached flows, pulsating flows, and swirling flows, to clarify the mechanisms of heat transfer.
(A part of this work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 22560214 and 16K06142.)
【 main literature 】
- Spatio-Temporal Measurement of Convective Heat Transfer Using Infrared Thermography, InTech open (2011)
- Unsteady Heat Transfer for a Turbulent Flow Measured Using Infrared Thermograph, J. Visualization Society of Japan, 29-113 (2009), 116-121
- Development of spatiotemporal heat transfer measurements in wall-bounded flows, European Mechanics Society (Euromech) Colloquium 631 (Keynote Lecture), (2024), from the presentation slides
Boiling Heat Transfer Measurements Using Infrared Thermography
【 概要 】
We have also been working to measure the fast and complex heat transfer fluctuations due to boiling with high spatiotemporal resolution using high-speed infrared thermography in order to clarify the mechanism of boiling heat transfer.
(A part of this work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 21K03908.)

Studies on Thermal Design of Electronic Equipment
【 Outline 】
According to the progress of performance and miniaturization of electronic devices, the heat density of such devices continues to increase. Thus, cooling the devices has become an important issue. In our laboratory, we conducted basic studies on heat transfer from an air-cooled heating element placed in an enclosure, which simulates a compact electronic device. Also, in order to simplify the thermal design for the air-cooled device using CFD, the fan-curve model was improved to reproduce a realistic flow field at the discharge side of a fan with a small computational load.
(A part of this work was conducted as a part of the RC181, 202, 214, 227, 239, 248, 256 Research Projects, Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.)

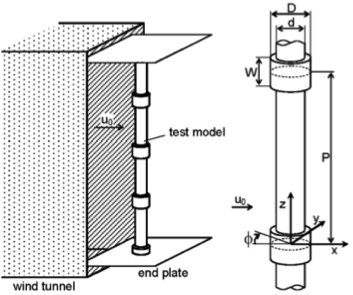
Suppression of Vortex Shedding from a Cylinder
【 Outline 】
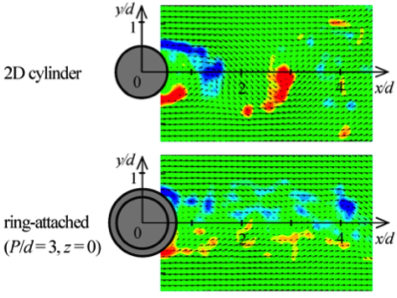
If a fluid flows across a cylindrical object, periodic vortex shedding (Karman vortex street formation) occurs and generates large drag and a fluctuating force. At the same time, it generates aerodynamic noise, called Aeolian tone. In our laboratory, we have studied a method to suppress vortex shedding by attaching axisymmetric projections, called “rings”, arranged in the axial direction of the cylinder. Since the ring-attached cylinder has axial symmetry, vortex shedding can be suppressed with respect to the flow in all directions perpendicular to the cylinder.
Experimental results show that if the configuration of rings is optimized, the periodicity in the fluctuating lift almost disappears for a Reynolds number higher than 20,000, with a reduction of drag. In order to clarify this mechanism, we have conducted measurements of the wake and flow visualization.
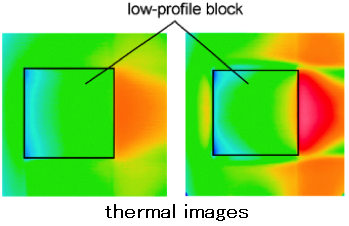
Forced Convection Heat Transfer Around an Object
【 Outline 】
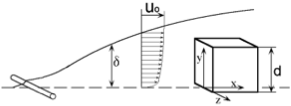
We have measured the local heat transfer distribution around an object with a basic shape, such as a circular cylinder or a wall-mounted cube, and have examined the correspondence between the flow field and heat transfer. The data obtained in these experiments can be used for thermal design of equipment and to validate CFD models.

【 main literature 】
- Local Heat Transfer around a Wall-Mounted Cube in the Turbulent Boundary Layer, Int. J. Heat and Mass Transfer, 44-18 (2001), 3385-3395
- Local Heat Transfer around a Wall-Mounted Cube at 45 Degree to the Flow in the Turbulent Boundary Layer, Int. J. Heat and Fluid Flow, 24-6 (2003), 807-815
- Heat Transfer in Separated Flow Behind a Circular Cylinder for Reynolds Numbers from 120 to 30000 (2nd Report, Unsteady and Three-Dimensional Characteristics), JSME Int. J., Ser.B, 47-3 (2004), 622-630
- Unsteady Heat Transfer from a Circular Cylinder for Reynolds Numbers from 3000 to 15,000, Int. J. Heat and Fluid Flow, 25-5 (2004), 741-748
- Variation of Nusselt Number with Flow Regimes Behind a Circular Cylinder for Reynolds Numbers from 70 to 30000, Int. J. Heat and Mass Transfer, 47-23 (2004), 5169-5173