PROJECTS
Surgical Simulators
Development of encountered-type haptic interface for surgical simulators
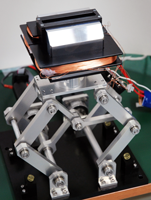
Surgical simulators using virtual reality is a promising technology for studying surgical plans and improving surgical techniques in the medical field. A surgical simulator allows for a more realistic surgical experience by using an haptic interface to provide feedback to the operator about the reaction force generated in surgical operations performed on a virtual human body and implemented on a computer. Owing to their importance, simulators with various types of haptic interfaces have been developed. Surgical instruments come in various shapes; as a result of this, a simple method to feedback the reaction force is to mount the surgical instrument on the haptic interface. However, if the instrument is mechanically attached, the changing of instruments, which is normal in real operations, becomes difficult. In view of this, this research is developing a haptic interface that allows for ease of changing of instruments. In this device, magnetorheological (MR) fluid is used to simulate body organs, allowing operations, such as resection, to be performed directly using an instrument on the MR fluid.
Development of simulation software for brain surgery
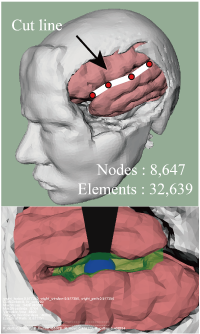
In recent years, the development of sophisticated surgical techniques has saved many lives and improved postoperative quality of life. However, it is very difficult for a physician to keep up-to-date with the latest treatment methods; this calls for new environments where new surgical techniques can be learnt efficiently. In conventional methods where training is carried out using animals or surgical trainers made of rubber, the training can be carried out only for a limited number of times. Moreover, it is not possible to train on special cases of diseases. In view of this, the development of surgical simulators using virtual reality is actively being undertaken. In this research, a virtual human body is simulated in a computer, and simulation software is developed to perform surgical operations in a virtual environment.
Humanoid Robots
Research on motor intelligence
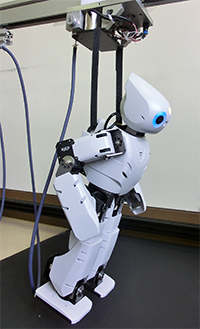
Humanoid robots that are built to resemble the human body shape are considered promising in performing various everyday tasks on behalf of human beings. Humanoid robots can walk on legs and perform human-like operations using the arm. Therefore, unlike the robotic arms for industrial use, they can autonomously move around in the working field. Moreover, they are also equipped with numerous joints, facilitating complex operations. However, since the humanoid is not fixed to the ground, it is highly likely that it may fall if an external force is applied to it. The purpose of this research is to skillfully generate an impact force through whole-body coordination while avoiding or minimizing the risk of falling or damaging when an external force is applied to the humanoid.
HILS (Hardware-In-the-Loop-Simulator) for developing articulated robots
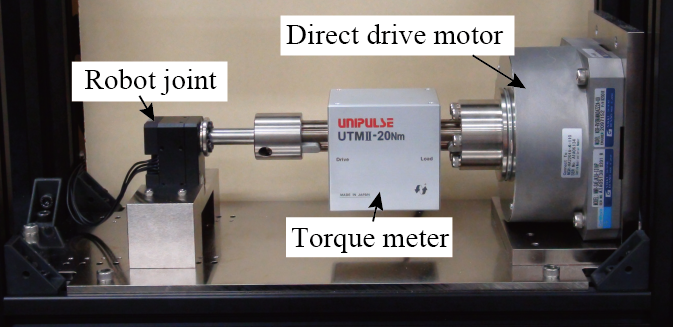
In the current robot development flow, it is difficult to accurately predict the behavior of a real robot only by numerical simulation. Therefore, it is necessary to repeat the process, such as making a prototype, test it, and improving it. This process extends the development term and increases the cost of the development. In this study, we focus on the robot joint, which is one of the difficult elements to model in the numerical simulation, and propose a simulation method which does not require modeling of the joint. By this, it becomes possible to accelerate the design of the joint mechanism of the next generation robot such as the flexible joint in which the modeling is difficult.